Building Robust Algorithmic Trading Systems
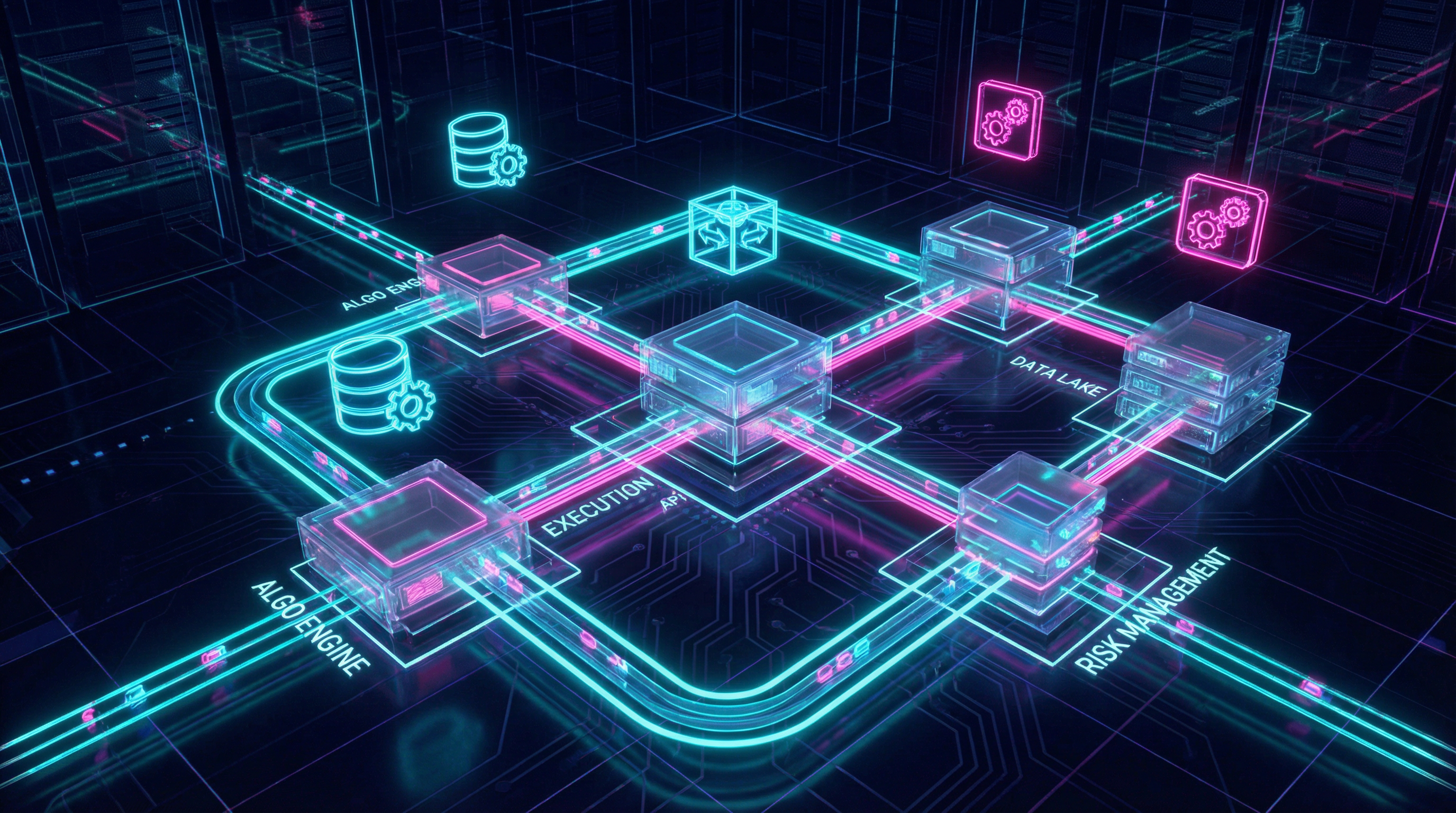
Production algorithmic trading systems require careful architectural design to handle the demands of real-time market data processing, rapid decision-making, and reliable order execution. Unlike research environments where performance and reliability are secondary concerns, production systems must operate continuously with minimal downtime while managing risk and maintaining accurate state across market disruptions.
Event-Driven Architecture
Event-driven design forms the foundation of modern trading systems, processing market data and generating trading signals through asynchronous event handlers. This architecture naturally models financial markets where prices, orders, and fills arrive as discrete events. Each component responds to relevant events without blocking, enabling high throughput and low latency critical for competitive execution.
The event loop receives market data updates, order confirmations, and system notifications, dispatching them to appropriate handlers. Strategy logic subscribes to specific event types—such as price updates for monitored instruments—and publishes trading decisions as new events. This decoupling allows strategies to focus on alpha generation while infrastructure handles execution mechanics.
Message queues buffer events during processing spikes, preventing data loss when market activity surges. Persistent queues enable system recovery after crashes by replaying missed events, reconstructing state to resume trading seamlessly. Priority queues ensure critical events like risk limit breaches receive immediate attention over routine market data updates.
Risk Management Integration
Risk management must be deeply integrated into trading system architecture rather than bolted on as an afterthought. Pre-trade risk checks validate every order against position limits, concentration constraints, and available capital before submission. These checks execute synchronously in the critical path, blocking orders that would violate risk parameters regardless of strategy logic.
Real-time position tracking maintains accurate views of current exposure across all instruments and strategies. Position reconciliation compares internal state against exchange reports, detecting discrepancies that might indicate execution issues or system bugs. Automated alerts notify operators of unusual activity requiring investigation.
Circuit breakers halt trading when predefined thresholds are exceeded, protecting capital during system malfunctions or extreme market conditions. Loss limits trigger automatic position liquidation if drawdowns reach unacceptable levels. Volatility filters pause strategies when market conditions deviate from historical norms used during backtesting.
State Management and Persistence
Trading systems must maintain consistent state across restarts, network disruptions, and exchange outages. Critical state—including open positions, pending orders, and strategy parameters—persists to disk after every modification. Upon restart, systems reconstruct state from persistent storage, querying exchanges to confirm current positions and outstanding orders.
Database selection balances consistency requirements against performance constraints. Time-series databases efficiently store market data and performance metrics for analysis. Relational databases track orders and positions with ACID guarantees. In-memory databases accelerate hot path operations while asynchronously replicating to durable storage.
State machines formalize strategy logic, explicitly defining valid states and transitions. This approach prevents logical errors where strategies enter undefined states during unusual market conditions. State machine visualization aids debugging and helps new team members understand system behavior.
Infrastructure and Deployment
Production deployment requires infrastructure supporting high availability and disaster recovery. Redundant servers in geographically distributed data centers protect against localized failures. Automated failover mechanisms detect primary system failures and activate standby systems within seconds, minimizing trading interruptions.
Monitoring systems track key performance indicators including latency percentiles, order fill rates, and strategy P&L. Anomaly detection algorithms identify unusual patterns requiring investigation before they escalate into serious issues. Comprehensive logging captures system behavior for post-incident analysis and regulatory compliance.
Deployment pipelines automate testing and rollout of system updates. Staging environments mirror production configurations, enabling realistic testing of changes before deployment. Canary releases gradually shift traffic to updated systems, allowing quick rollback if issues emerge. Blue-green deployments maintain two identical production environments, switching traffic between them for zero-downtime updates.
Performance Optimization
Latency optimization focuses on the critical path from market data receipt to order submission. Profiling identifies bottlenecks consuming excessive time or CPU cycles. Lock-free data structures reduce contention in multi-threaded components. Memory pools eliminate allocation overhead in hot paths.
Network optimization reduces round-trip times to exchanges through co-location and optimized routing. Kernel bypass techniques like DPDK minimize operating system overhead in packet processing. Custom network protocols eliminate unnecessary headers and serialization overhead for internal communication.
The cryptocurrency market's 24/7 nature demands systems that operate reliably for extended periods without manual intervention. Automated health checks detect degraded performance before complete failures occur. Self-healing mechanisms restart failed components and clear transient errors. Comprehensive documentation enables rapid diagnosis and resolution of issues requiring human intervention.